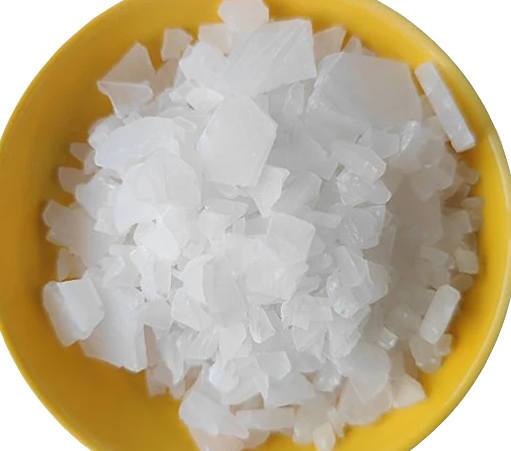






Aluminum sulfate(Polyaluminum sulfate) is a widely used inorganic coagulant for drinking water purification, industrial wastewater treatment, paper sizing, dyeing wastewater treatment, and sludge dewatering.
It forms aluminum hydroxide flocs during hydrolysis, which quickly adsorb suspended solids, colloids, organic pollutants, and heavy metal ions, achieving fast settling and efficient water clarification.
| Description | Parameters | |
| Superior Grade | First Grade | |
| Alumina Al2O3 %≥ | 18.5 | 17.5 |
| Iron oxide Fe2O3 %≤ | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Water insoluble content %≤ | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Ph Value 1% aqueous solution | 4.0 | 4.0 |
| Arsenic(As)%≤ | 0.0002 | 0.0002 |
| Heavy metals(with pb)%≤ | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| CAS NO | 10043-01-3 | |
| Place of Origin | Henan, China | |
| Brand Name | Lvyuan | |
| Product name | Aluminum sulfate Polyaluminum sulfate | |
| Effective storage life | 24 month | |




Aluminum Sulfate, also known as Polyaluminum Sulfate, is a widely used inorganic polymer coagulant. It plays essential roles in water treatment, paper making, dyeing, and various industrial applications. Its main application fields include:

Dilution
Prepare a 5–10% solution of aluminum sulfate and stir until completely dissolved.
Dosing Method
Drinking water treatment: Perform jar tests to determine optimal dosage (typically 10–50 mg/L).
Wastewater treatment: Adjust dosage according to COD, turbidity, and oil content (typically 50–300 mg/L).
Co-use with coagulant aids: Often used together with PAM to strengthen floc formation.
Coagulation Process
Rapid mixing (30–60 seconds) Moderate mixing (3–5 minutes) Slow mixing to form large flocs (10–15 minutes) Sedimentation or flotation
Always perform jar tests to determine optimal dosage and pH range. Store separately from strong alkalis to prevent decomposition.
Keep in a dry, cool place away from direct sunlight. Avoid metallic containers; use corrosion-resistant tanks (PVC/PE).
For drinking water applications, ensure the product meets potable water grade standards.
Avoid overdosing to prevent excessive residual aluminum in treated water.
Q1: How effective is aluminum sulfate in water treatment?
A1: It forms flocs quickly, settles fast, and effectively removes turbidity and suspended solids.
Q2: What is the difference between aluminum sulfate and PAC?
A2: Aluminum sulfate is cost-effective and suitable for stable water quality; PAC produces stronger flocs and less sludge.
Q3: Can aluminum sulfate be used for high-COD wastewater?
A3: Yes, but for best performance, it is often combined with PAC, PAM, or decolorizing agents.
Q4: Is aluminum sulfate safe for drinking water treatment?
A4: Yes, as long as drinking-water-grade aluminum sulfate is used and dosage is properly controlled.
Q5: How to determine the correct dosage?
A5: Run jar tests considering turbidity, pH, oil content, and other water quality factors.
Please contact us for free quotation by form below. We promise the quickest response within 24 hours: