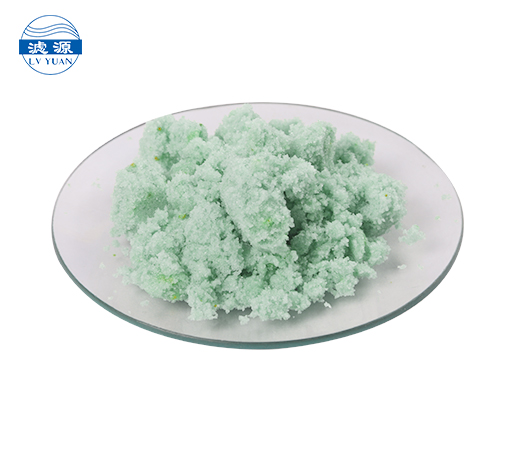








Ferrous Sulfate Heptahydrate (Ferrous Sulphate Heptahydrate) commonly known as “green vitriol”, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula FeSO4·7H2O. It can adjust the pH value of alkaline water, organically combine with suspended matter in water, and accelerate precipitation. It is mainly used for water purification and industrial wastewater treatment, and also has a bactericidal effect.
|
Description |
Parameters |
Description |
Parameters |
|
CAS NO. |
7720-78-7 |
Usage |
water purification and industrial wastewater treatment |
|
Color |
Light green |
Type |
Inorganic |
|
Grade |
Industrial Grade |
Odor |
Odorless |
|
FeSO4·7H2O % ≥ |
88 |
Corrosive: |
Non-corrosive |
|
TiO2 % ≤ |
1 |
EINECS No. |
231-753-5 |
|
Heavy metal content %≤ |
0.002 |
Brand Name |
Lvyuan |
|
Water insoluble content %≤ |
1.0 |
Product name |
Ferrous Sulfate Heptahydrate (Ferrous Sulphate Heptahydrate) |
|
Arsenic (AS) %≤ |
0.0005 |
Package |
25KGS/PVC or 50KGS/PVC with 2 inner layers |
|
Free acid (calculated as H2SO4) %≤ |
2.0 |
Effective storage life |
12 month |
|
Place of Origin |
Henan, China |
|
|
25KGS/PVC or 50KGS/PVC with 2 inner layers




Ferrous sulfate heptahydrate, also known as green vitriol, is a light blue-green monoclinic crystal with strong reducing properties. It is soluble in water and widely used in water treatment, agriculture, feed, chemicals, electroplating, and other industries. It is a versatile inorganic salt product.

Q1:What types of wastewater is Ferrous Sulfate Heptahydrate suitable for?
A1:Ferrous sulfate heptahydrate is widely used in the treatment of various wastewater types, including:
-Municipal sewage
-Industrial wastewater (metallurgy, electroplating, paper mills, dyeing, etc.)
-Agricultural runoff
Wastewater with high phosphorus, turbidity, or color
It has strong effects in flocculation, decolorization, phosphorus removal, and heavy metal reduction, especially suitable for neutral to mildly alkaline wastewater.
Q2: What are the benefits of using Ferrous Sulfate Heptahydrate together with PAC?
A2:The combined use of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (FeSO₄·7H₂O) and polyaluminum chloride (PAC) offers significant synergistic effects:
|
Comparison |
PAC Only |
PAC + Ferrous Sulfate |
|
Floc size |
Good |
Larger, denser flocs |
|
Decolorization |
Moderate |
Significantly improved |
|
Heavy metal removal |
Limited |
Strong removal of Fe, Mn, Cu, etc. |
|
Phosphorus removal |
Partial |
Up to 90% phosphate removal |
|
COD reduction |
Fair |
Enhanced with combination |
Recommended order: Add ferrous sulfate first, then PAC, and optionally PAM for better sedimentation and clarification.
Q3: Can Ferrous Sulfate Heptahydrate be used together with PAM?
A3: :Yes. Ferrous sulfate and polyacrylamide (PAM) work well together in water treatment:
-Ferrous sulfate acts as a coagulant and heavy metal binder
-PAM serves as a flocculant aid, promoting solid-liquid separation and improving sludge dewatering
-Anionic PAM is usually recommended for wastewater containing suspended solids
Recommended sequence: FeSO₄ → PAC (optional) → diluted PAM solution → sedimentation tank
Q4: What is the optimal pH range for dosing Ferrous Sulfate Heptahydrate?
A4: The optimal pH range is 4.5–9.0.
In strongly alkaline conditions (pH > 9), Fe²⁺ may form Fe(OH)₃ precipitate prematurely, reducing treatment efficiency. Adjust pH if necessary before dosing.
Q5: How to determine the appropriate dosage of Ferrous Sulfate Heptahydrate?
A5: Dosage should be determined based on jar testing to match actual water quality conditions
Typical dosage ranges:
-Drinking water: 20–50 mg/L
-Industrial wastewater: 50–300 mg/L
-Phosphorus removal: Fe:P molar ratio of 1:1 or 2:1
Every type of wastewater differs; pilot testing ensures optimal treatment results.
Please contact us for free quotation by form below. We promise the quickest response within 24 hours: